Mercury, the smallest and innermost planet in our solar system, has long intrigued scientists and stargazers alike. This unassuming celestial body holds many secrets and surprises that are waiting to be uncovered. In this article, we will explore 16 fascinating facts about Mercury that will leave you in awe of its unique characteristics and place in the cosmos.
1. Size and Distance
Mercury is a relatively small planet, with a diameter of about 4,880 kilometers. It is the closest planet to the Sun, with an average distance of about 57.9 million kilometers. Despite its proximity to the Sun, Mercury is not the hottest planet in the solar system. That title belongs to Venus, due to its thick atmosphere.
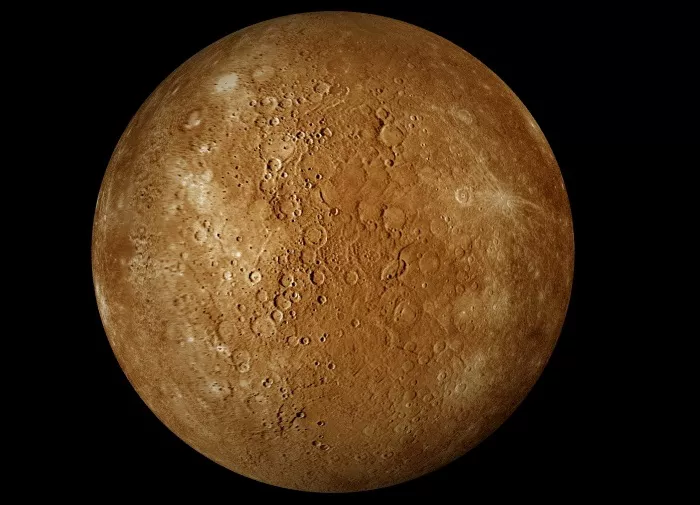
2. Surface Features
The surface of Mercury is covered with craters, mountains, and plains. Some of the craters are so large that they can be seen from Earth with a telescope. The planet also has a unique feature called the Caloris Basin, which is one of the largest impact basins in the solar system.
3. Atmosphere
Mercury has a very thin atmosphere, consisting mainly of helium, hydrogen, and oxygen. This atmosphere is so thin that it is almost negligible compared to the atmospheres of other planets.
4. Temperature Extremes
Due to its proximity to the Sun, Mercury experiences extreme temperature variations. During the day, the surface temperature can reach up to 427 degrees Celsius, while at night it can drop to as low as -173 degrees Celsius.
5. Magnetic Field
Mercury has a weak magnetic field, which is thought to be generated by a dynamo effect in its molten core. This magnetic field is much weaker than that of Earth, but it is still significant enough to protect the planet from some of the solar wind.
6. Orbit
Mercury has an elliptical orbit around the Sun, which means that its distance from the Sun varies throughout its year. This also causes the planet to experience significant changes in temperature and illumination.
7. Rotation and Revolution
Mercury has a very slow rotation period of about 59 Earth days. However, its revolution around the Sun is much faster, taking only 88 Earth days. This means that a day on Mercury is almost twice as long as a year.
8. Tides
The gravitational pull of the Sun and other planets causes tides on Mercury. These tides are much smaller than those on Earth, but they still have an impact on the planet’s geology.
9. Volcanism
There is evidence of past volcanic activity on Mercury. Some of the features on the planet’s surface, such as smooth plains and lava channels, suggest that volcanic eruptions may have occurred in the past.
10. Meteorites
Mercury has been bombarded by meteorites throughout its history. These impacts have left behind craters and other features on the planet’s surface.
11. Water Ice
There is evidence of water ice in some of the craters near the poles of Mercury. This ice is thought to have been deposited by comets or other celestial bodies.
12. Exploration
Mercury has been explored by several spacecraft, including Mariner 10 and Messenger. These missions have provided valuable insights into the planet’s geology, atmosphere, and magnetic field.
13. Composition
Mercury is believed to be made up mainly of iron and silicate rocks. Its high density suggests that it has a large iron core.
14. Rings
Mercury is one of the few planets in our solar system that does not possess rings. Rings around planets are usually made up of particles of various sizes, ranging from dust to large chunks of ice and rock. The absence of rings around Mercury can be attributed to several factors.
One possible reason is Mercury’s relatively small size and gravitational pull. Planets with stronger gravity are more likely to attract and hold onto debris that could form rings. Mercury’s gravity is not strong enough to capture and maintain a significant amount of material in orbit around it.
Another factor could be the planet’s proximity to the Sun. The intense heat and solar wind near Mercury may have prevented the accumulation of ring material. Any small particles that might have tried to form a ring would likely be blown away by the solar wind or vaporized by the intense heat.
The lack of rings also makes Mercury stand out among its planetary neighbors. Saturn, for example, is famous for its extensive and beautiful ring system. Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune also have faint ring systems. In contrast, Mercury’s clean orbital path gives it a distinct appearance.
This absence of rings also has implications for our understanding of planetary formation and evolution. It suggests that the processes that led to the formation of rings around other planets did not occur or were not as effective in the case of Mercury. Studying Mercury’s lack of rings can help scientists gain insights into the diverse ways in which planets develop and change over time.
15. Moons
Mercury does not have any natural moons.
16. Visibility
Mercury is visible from Earth with the naked eye, but it is often difficult to spot due to its proximity to the Sun.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mercury is a fascinating planet with many unique characteristics. From its extreme temperature variations to its thin atmosphere and weak magnetic field, Mercury offers a wealth of scientific mysteries to be explored. As we continue to study this small but remarkable planet, we are sure to uncover even more fascinating facts about its past, present, and future. Whether you are a stargazer or a scientist, Mercury is a planet that is sure to capture your imagination and inspire further exploration of the cosmos.
Related topics: